Guide: Battery internal resistance – what, why and how?
What is the battery internal resistance?
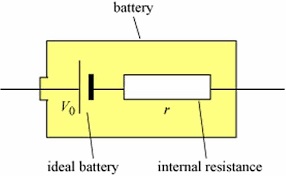
Every battery, no matter what type it is, has some internal resistance. Sometimes battery is schematicaly drawn as voltage source in series with some resistance.
The internal resistance of a battery is dependent on its size, capacity, chemical properties, age, temperature, and the discharge current.
Internal resistance gets lower when the battery temperature increases. Thats why the cold winter weather reduces the power and capacity delivered by the bettery. It is useful to have the batteries pre-warmed when using them in the cold environment.
Why should I be interested in the battery internal resistance?
In rechargeable lithium polymer (LiPo) batteries, the internal resistance is largely independent of the state of charge but increases as the battery ages; thus, it is a good indicator of expected life. If the internal resistance increases on one of the battery cells this means the battery will supply less current and will probably heat up more than it should.
There is a direct connection between the battery internal resistance and the C-rating of the battery pack. Typically the high C-rating batteries have lower internal resistance values.
How to measure the battery internal resistance?
The scientific method would be connecting the battery in a circuit with a resistor, measuring voltage through the battery, calculating current, measuring voltage through the resistor, finding the voltage drop and, using the kirchoff law, calculating the remaining resistance which would be the internal resistance.
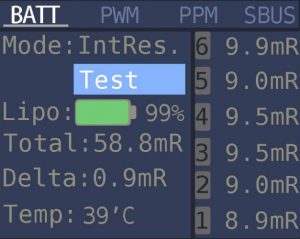
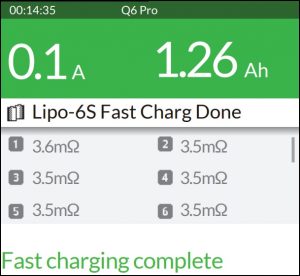
Another, much more easier method is to use the battery charger that has battery internal resistance measurement function. Some chargers have a dedicated internal resistance (IR) measurement function (examples of such chargers: ToolkitRC M8, M6, M600) and some can measure IR while charging the battery (examples of such chargers: ISDT Q6 Lite, Q6, Q8).
Why the battery Internal Resistance degrade?
Because of:
- The charge-discharge cycle inevitably lead to Internal Resistance degradation. The more you use the more the battery degrades.
- Battery ages. Battery degrades even if you are not using it. So better use it – go and fly as frequent as you can 🙂
- Storing the battery in the fully discharged of fully charged state leads to rapid internal Resistance degradation.
- Extreme discharging (or overcharging) also leaves instant
- Overheating (not speaking about normal warm state) the pack also leads to change in chemical battery substance, puffing and increase of the internal resistance.
Tips and recomendations on Internal Resistance of the battery
- The internal resistance value should be the same or very similar for all the battery cells. If at least one of the battery cell’s IR will increase, the whole pack performance will degrade.
- The higher the internal resistance the less current the battery is capable to provide.
- The higher the internal resistance the more the battery will heat up on the same current output.
- Write down the new battery pack internal resistance values on the battery so you can have a reference in the future and you will know when the battery pack will start to degrade.
- Batteries that have high internal resistance will take more time to fully charge. Also batteries with the lower internal resistance usually can be charged up with the higher current setting (2C – 5C rates).


Thank you for a very clear explanation. I originally wanted simple method of sorting out the life length of my Ryobi 18v tool batteries and your article is a great help.
I have one question more for curiosity, I did the same test on a 12v car battery (lead acid) and got a zero resistance reading…..is this due the construction type?
I tested the same battery using both a high discharge tester and an electronic car battery tester and both test said the battery is good (but that’s all they say).
Hi, a working battery can’t have zero internal resistance. If the battery had zero resistance it would be shorted. Actually it happens sometimes. For instance LiPo batteries may became shorted if discharged too low. This is due the growth of so called dendrites in the battery between the layers.

Most probably the measurement instruments you used are not able to measure the Lead Acid battery internal resistance accurately.
Here is what I’ve found about the Lead Acid battery internal resistance:
Lead Acid Battery – the lower the battery internal resistance the more the battery in good condition.
To be exact, for a 12V Lead Acid Battery,
If IR>30 milliohm, battery is in very bad condition. Probably unusable.
If IR is between 10 to 30 milliohm, still poor condition but may be usable or revivable.
If IR is between 5 to 10 milliohm, it is in good condition.
If IR is less than 5 milliohm, it is in very good condition.
But all this given criteria are just an estimate and does not guarantee the battery condition. As the condition depends upon some other factors too.